Theme: Battle Together For A Cancer Free World
Oncologists 2019
Conference Series LLC LTD invites all the oncologists and the cancer researchers across the globe to attend the much awaited 23rd Global Annual Oncologists Meeting scheduled on July 15-16, 2019 at Yokohama, Japan, which is the part of our Oncology Series Conferences. The 23rd Global Annual Oncologists Meeting aims to brings together the Oncology Researchers, Oncologists, Oncology Surgeons, Surgical Oncologists, Radiologists, Oncology Pathologists, Pathologists, Immune Oncology Therapists, Nurses, health workers, Multidisciplinary Oncology Specialists or Oncologists working in the area of various Organ Specific Cancers like: Breast Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Colon Cancer, Brain tumours, blood cancers, urological cancer specialists, lung cancer specialists etc. The Cancer Experts to be gather here are basically from industry, hospitals, cancer centres and academia with the aim to discuss the current issues, trends including future innovations and strategies in the broad area of Cancer research. The extent of meeting covers all fields of malignancies.
Theme: “Battle Together For a Cancer Free World”
The scope of conference covers all fields of cancers. The sessions are designed in such a way that, it will cover the current trends and challenges in the Diagnosis, treatment and management of all cancer types, but not limited to: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL), Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML), Adrenocortical Carcinoma, Anal Cancer, Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancer, Bile Duct Cancer, Bladder Cancer, Bone Cancer, Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors, Breast Cancer, Castleman Disease, Cervical Cancer, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL), Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML), Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukaemia (CMML), Colorectal Cancer, Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS), Endometrial Cancer, Oesophagus Cancer, Ewing Family of Tumors, Eye Cancer, Fallopian Tube Cancer, Fibrous Histiocytoma of Bone, Malignant, and Osteosarcoma, Gallbladder Cancer Gastrointestinal Carcinoid Tumors, Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST), Hodgkin Lymphoma, Head and Neck Cancer, Hepatocellular (Liver) Cancer, Histiocytosis, Langerhans Cell, Hypo pharyngeal Cancer, Intraocular Melanoma, Islet Cell Tumors, Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors, Kaposi Sarcoma, Laryngeal and Hypo pharyngeal Cancer, Leukaemia, Liver Cancer, Lung Cancer, Lung Carcinoid Tumor, Lymphoma, Lymphoma of the Skin, Melanoma Skin Cancer, Merkel Cell Skin Cancer, Multiple Myeloma, Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses Cancer Nasopharyngeal Cancer, Neuroblastoma, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, Lung Cancer, Oral Cavity and Oropharyngeal Cancer, Osteosarcoma, Ovarian Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Penile Cancer, Pituitary Tumors, Prostate Cancer, Plasma Cell Neoplasm/Multiple Myeloma, Pheochromocytoma, Paranasal Sinus and Nasal Cavity Cancer, Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (Islet Cell Tumors), Rectal Cancer, Renal Cell (Kidney) Cancer, Retinoblastoma, etc.
Conference Highlights
Oncology
Medical Oncology
Surgical Oncology
Radiation Oncology
Sub-specialties in Oncology
Cancer Screening
Clinical Trials and New Anti-cancer Drug development
Cancer Pharmacology
Cancer Genetics
Oncology Nursing
Cancer Epidemiology
Cancer: Life style and Nutrition
Targeted Anti-Cancer Therapies
Target Audience
Oncologists
Radiologists
Immunologists
Pathologists
Molecular Biologists
Clinical Oncology Researchers
Oncology Nurses
Cancer Researchers
Young Researchers
Undergraduates
Biomarker Associations and Societies
Business Entrepreneurs
Pharmaceutical Companies
Diagnostics Companies
Track 1: Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medication that arrangements with the anticipation, analysis, and treatment of growth. A therapeutic expert who hones oncology is an oncologist.
The three parts which have enhanced survival in malignancy are:
Avoidance – by decrease of hazard factors like tobacco and liquor utilization
Early conclusion – screening of regular cancers and thorough analysis and arranging
Treatment – multi methodology administration by talk in tumor board and treatment in an exhaustive disease focus.
Screening
Blood cancer
Lymphoma
Solid tumors
Track 2: Immunooncology and Cancer Immunotherapy
Cancer immunology is a branch of immunology that studies interactions between the immune system and cancer cells (also called tumors or malignancies). It is a field of research that aims to discover cancer immunotherapies to treat and retard progression of the disease. Cancer immunotherapy also known as Immuno-oncology is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies can be categorized as active, passive or hybrid (active and passive). The immune response, including the recognition of cancer-specific antigens, forms the basis of targeted therapy (such as vaccines and antibody therapies) and tumor marker-based diagnostic tests.
Surgery
Chemotherapy
Radiation
Targeted therapy
Immuno-oncology
Track 3: Cancer: Lifestyle and Nutrition
Many factors influence the development of cancer. Over the last 25 years, science has shown that diet, physical activity, and body weight—especially being overweight or obese—are major risk factors for developing certain types of cancer. Around a third of the most common cancers could be prevented through lifestyle changes. The main behavioral and environmental risk factors for cancer mortality in the world are related to diet and physical inactivity, use of addictive substances, sexual and reproductive health and exposure to air pollution and use of contaminated needles. The body’s ability to resist cancer may be helped by following a healthy diet, staying physically active, and avoiding excess body fat. Cancer and cancer treatments can also affect your body's ability to tolerate certain foods and use nutrients.
Body weight, physical activity and cancer
Endogenous hormones and cancer
Mechanisms of nutritional carcinogenesis and anti-carcinogenesis
Trials on the dietary prevention of cancer
Gene-nutrient interactions
Cancer prevention: global implications of new European evidence
Track 4: Oncology Nursing and Care
Oncology Nursing is a field involving practice encompasses the roles of direct caregiver, educator, consultant, administrator, and researcher. Oncology and cancer nursing extends to all care delivery settings where clients experiencing or at risk for developing cancer receive health care, education, and counseling for cancer prevention, screening and detection. It also involves appropriate screenings and other preventative practices, symptom management, care to retain as much normal functioning as possible, and supportive measures upon end of life.
Oncology APN
Oncology RN
Primary palliative care
Specialty palliative care
Track 5: Cancer Screening
Unlike diagnostic efforts prompted by symptoms and medical signs, cancer screening involves efforts to detect cancer after it has formed, but before any noticeable symptoms appear. This may involve physical examination, blood or urine tests or medical imaging.
Cancer screening is not available for many types of cancers. Even when tests are available, they may not be recommended for everyone. Universal screening or mass screening involves screening everyone. Selective screening identifies people who are at higher risk, such as people with a family history. Several factors are considered to determine whether the benefits of screening outweigh the risks and the costs of screening.
These factors include:
Possible harms from the screening test: for example, X-ray images involve exposure to potentially harmful ionizing radiation
The likelihood of the test correctly identifying cancer
The likelihood that cancer is present: Screening is not normally useful for rare cancers.
Screening mammography
Prostate Cancer Screening
Pancreatic Cancer Screening
Oral Cancer Screening
Lung Cancer Screening
Track 6: Metastasis and Drug Resistance
Investigations of growth attack/metastasis and medication opposition have in the past for the most part continued along the different pathways of research. As of late, nonetheless, intrigue has been centered on the conceivable connection between sedate obstruction and growth intrusion and metastasis.
Metastasis
MDR and Calcium Channel Blockers
Apoptosis
Animal models
Track 7: Targeted Cancer Therapies
Targeted therapy is a special type of chemotherapy that exploits differences between normal cells and tumor cells. It's occasionally utilized alone, however frequently other disease medicines are utilized with targeted therapy. As the name proposes, targeted therapies interfere with particular proteins engaged with tumor genesis. Instead of utilizing expansive base growth medications, concentrating on particular atomic changes which are one of a kind to a specific disease, directed tumor treatments might be all the more remedially gainful for some malignancies, including lung, colorectal, breast, lymphoma and leukemia.
Targeted drugs can work to:
Block or turn off chemical signals that tell the cancer cell to grow and divide
Change proteins within the cancer cells so the cells die
Stop making new blood vessels to feed the cancer cells
Trigger your immune system to kill the cancer cells
Carry toxins to the cancer cells to kill them, but not normal cells
Monoclonal antibodies
Small molecule drugs
Targeted therapy for breast cancer
Targeted therapy for Colorectal Cancer
Targeted therapy for Lung Cancer
Targeted therapy for Melanoma
Challenges of targeted therapies
Track 8: Oncology Nursing
An oncology nurse is a nursing professional who specializes in caring for people with cancer. Oncology nurses often serve as your first line of communication, and help coordinate the many aspects of your care throughout cancer treatment. Nursing Management is an important chapter of the nursing education. The nursing professionals in radiation oncology field will be highly demandable. Oncology nursing professionals mostly gives the palliative care for patients and comforts them. Cancer Congress 2018 will create a new revolution in cancer science and cancer nursing field.
Nursing education
Nursing Management
Clinical Nursing
Critical Care
Continuing Nursing Education
Track 9: Pharmaceutical Oncology
A multidisciplinary approach to overhaul has been applied in a variation of settings in clinical oncology, particularly among patients with stomach and colorectal cancer. Multidisciplinary care incorporates various disciplines that existing resources to enhance treatment plans and develops patients’ worth of life. Although the contribution of clinical pharmacists as part of the multidisciplinary team in the oncology department. Cancer Drugs were applied in order to treat the cancer and reducing symptoms of the cancer, and side-effects, such as nausea. Doctors would treat the cancer patients with two or more drugs that were used in chemotherapy and rarely with other medicines, such as steroids. Anti-cancer drugs eliminate cancer cells by preventing growth or obstructing multiplication at certain point in their life cycles. Vaccines were medicines that develops the immune system's natural ability to safeguard the body from “foreign invaders,” that mainly forms an infectious agents that may cause hereditary disease. HPV vaccine and Hepatitis B vaccine were cancer prevention vaccines supported by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Cancer treatment vaccines were also called therapeutic vaccines that increase the capability of immune system to acknowledge and abolish the antigens.
Theoretical Medicines
Anti-Metabolite Drugs
Alkylating Agents
Microtubule Inhibitor
Steroid Hormones
Miscellaneous Agents
Natural Agents
HMT Inhibitors
Biological Respond Modifier
Track 10: Cancer biopsy
A biopsy is the evacuation of a little measure of tissue. It is an imperative way specialists analyze a wide range of sorts of growth. After a biopsy, your social insurance group finishes a few stages previously the pathologist makes a conclusion. A pathologist is a specialist who works in deciphering research facility tests and assessing cells, tissues, and organs to analyze illness.
Hyperplasia
Dysplasia
Neoplasia
Sarcoma
Track 11: Oncogenomics
Oncogenomics is a sub-field of genomics that describes disease related qualities. It centers around genomic, epigenomic and transcript modifications in cancer. Cancer is a hereditary malady caused by collection of DNA changes and epigenetic adjustments prompting over the top cell multiplication and neoplasm arrangement.
Genome sequencing
Transcriptomes
Whole genome sequencing
Databases for cancer research
Track 12: Metastasis and Drug Resistance
Investigations of growth attack/metastasis and medication opposition have in the past for the most part continued along the different pathways of research. As of late, nonetheless, intrigue has been centered on the conceivable connection between sedate obstruction and growth intrusion and metastasis
Metastasis
MDR and Calcium Channel Blockers
Apoptosis
Animal models
Track 13: Clinical Trials and New Cancer Drug Development
Clinical Trials are inquired about investigations that include individuals. Clinical Trials are the completing advance in a long procedure that starts with explore in a lab. Before any new treatment is utilized with individuals in Clinical Trials, scientists work for a long time to comprehend its impacts on Cancer cells in the lab and in creatures. They likewise attempt to make sense of the symptoms it might cause. Preliminaries are accessible for all phases of Cancer.
It is a legend that they are just for individuals who have propelled Cancer that isn't reacting to treatment.
Advancements in Clinical Trials for Drug Development
Preclinical and Clinical research for cancer therapies
Cancer Clinical trials data management
Guidelines for Cancer Clinical trials
Drug Discovery & Development
Track 14: Cancer Epidemiology
The study of disease transmission of malignancy is the investigation of the variables influencing growth, as an approach to derive conceivable patterns and causes. The investigation of growth the study of disease transmission utilizes epidemiological strategies to discover the reason for malignancy and to recognize and create enhanced medications.
Single nucleotide polymorphism
Glioma
Selenium
Track 15: Cancer Pharmacology
Pharmacology deals with action of drug in the body. Cancer Pharmacology deals with the drugs used in cancer treatment, their mechanism of action, their side effects and their mode of elimination. Combination of Drugs and their efficacy has been a major choice of research interest.
Cancer Drugs
Anti-cancer drugs mechanism of action
Cancer Drugs absorption and Distribution
Cancer Drugs Metabolism
Side Effects of Synthetic Drugs in Cancer Treatment
Cancer happens to be a leading worldwide problem, with ∼14 million recorded new cases every year. In the USA, for example, over 0.5 million people die from cancer every year, making cancer the 2nd cause of death. Important is the fact that the cancer prevalence has been increasing mostly due to the increased lifespan of people. While recent changes in lifestyle have an impact on the spread of cancer, about two-thirds of the increase in the rate of cancer is due to longevity.
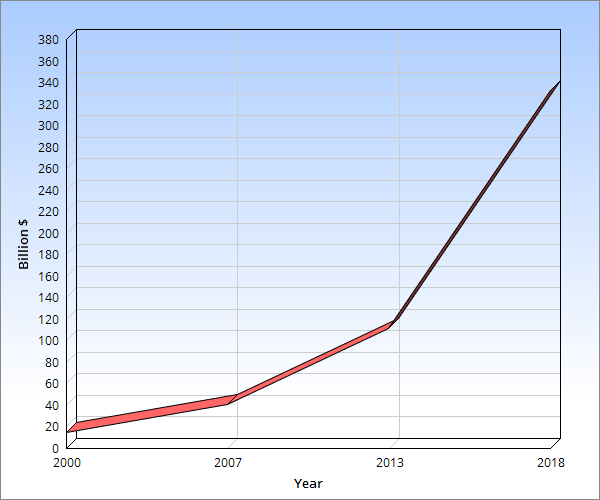
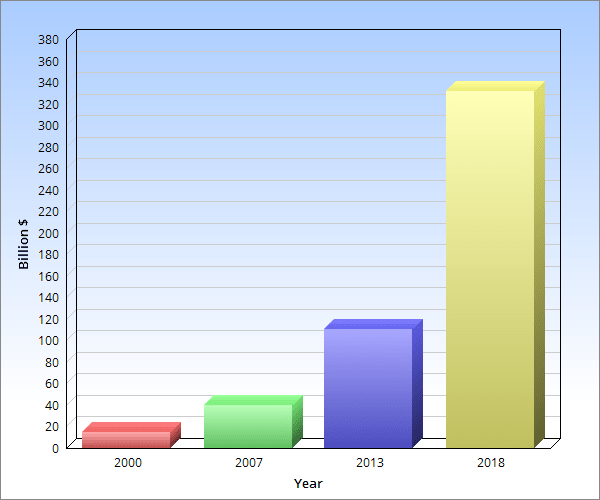
More than three-quarters of all people diagnosed with cancer in the UK are over the age of 60.3 Adding to the increasing cancer prevalence; there are several reasons that currently lead to an increase in the cancer therapy market. These include the availability and high development cost of better immunotherapy agents, the non-curable and lethal nature of most of the cancer forms, the reduced competition among agents as the use of an agent does not preclude from the concurrent/subsequent use of another one, that cheaper generics are often not considered as available alternatives to newer more costly agents but they are replaced by them, the earlier diagnoses and increased chronic management, the lack of magnitude threshold of drug benefit and increased insurance premiums due to unpredictable disease status. Between the years 2007 and 2013 for instance, the global cancer therapy market more than doubled, the global cancer therapy market increased from $40.0 billion in 2007 to an estimated $47.3 billion by the end of 2008 and $110.6 billion in 2013 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.5%.
This is a high annual growth rate of over 18%. Looking at the targeted therapy separately, which constitutes 45% of the cancer therapy market, this about tripled in within the same duration, increasing from combined market cost value of about $22 billion to almost 70 billion.
The total worldwide cancer drug market approached $14.8 billion in 2000. Growing at an average annual rate (AAGR) of 12.5%, this market exceeded $26.7 billion in 2005.
Established product lines currently constitute of nearly 90% of the global market, but will grow at only a rate of 6.6% AAGR through the period.
Innovative therapies, climbing at an AAGR of 40.2%, reached $8.6 billion in 2005, representing 32% of the total market.
Breast cancer therapy has the largest market with around $11.0 billion in sales in 2007. It increased to $12.0 billion in 2008 and $26.5 billion in 2013, by a CAGR of 16.4%.
Target therapy dominated in 2007 with a 45% share of the total cancer therapy market. This increased to 48% by 2008 and 62.5% in 2013.
There are ethical issues surrounding the comparative research on newer therapies for a dangerous disease like cancer, particularly the prospective research, which generally stems from the fact that exposing study participants to increased risk with experimental therapies may not actually be counterbalanced by clinical benefit. In comparative research, participants may, for example, be harmed by receiving a placebo instead of active treatment or, more commonly, participants stand the chance of receiving an experimental cancer therapy that will eventually turn out to be inferior to the best usual therapy available to patients. This is ethically problematic, given the recognized ethical principle that patients should receive the best-proven standard of care whenever feasible.
Conference Highlights
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | July 15-16, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by


