Suzanne Tinsley
Louisiana State University Health-Shreveport, USA
Title: Assistive technology utilized for cardiovascular conditioning for patients with spinal cord injury: A case study
Biography
Biography: Suzanne Tinsley
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: There are between 183,000 and 230,000 people with spinal cord injury (SCI) living in United States, with approximately 11,000 new cases each year. In spite of the advancements in medical and educational interventions, individuals with SCI still face health disparities and a number of challenges in maintaining cardiovascular health compared to the able bodied population. As a result, heart disease (HD) is one of the leading causes of death for patients with chronic SCI. Providing effective interventions to reduce the effects of HD for individuals with SCI is vital.
Purpose: Demonstrate the cardiovascular benefits of ambulation with a hybrid orthotic-functional electrical stimulation system (ARGO-FES) in a patient with paraplegia when performed in a clinical setting. Sample: Single-subject case study involving a patient with paraplegia enrolled in an outpatient rehab program for ambulation.
Method: Participant engaged in an ARGO-FES ambulation program 20 minutes, two times a week for six weeks. The following variables were measured at each session: pre- and post-exercise heart rate (HR) and blood pressures (BP) and distance ambulated. In addition, cholesterol (total, HDL/LDL ratio), and serum triglycerides were measured at baseline and at the end of the six-week intervention.
Findings: Patient demonstrated cardiovascular conditioning with reductions in post-ambulation HR and pulse pressure with an increase in distance ambulated. Triglycerides remained unchanged, LDL cholesterol decreased, and HDL cholesterol increased after six weeks of intervention.
Conclusion: Cardiovascular conditioning with an ARGO-FES system conducted in a clinical setting can reduce cardiovascular risk factors and facilitate health in individuals with chronic SCI.
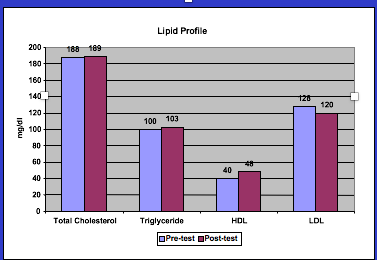
Figure: Pre- and post-exercise training total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL’s, and LDL’s blood lipid profile.
References:
- Cragg JJ, et al. (2015) Neuropathic pain, depression and cardiovascular disease: A national multicenter study. Neuroepidemiology 44(3):130-137
- Kerstin W, et al. (2006) What promotes physical activity after spinal cord injury? An interview study from a patient perspective. Disability & Rehabilitation 28(8):481-488.
- Bauman WA et al. (1998) The effect of residual neurological deficit on serum lipoproteins in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 36(1):13-17.
- Groah SL, Menter RR. (1998) Long-term cardiac ischemia leading to coronary artery bypass grafting in a tetraplegic patient. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 79(9):1129-1132.
- Solomonow M et al. (1997) Reciprocating gait orthosis powered with electrical muscle stimulation (RGO II). Part II: Medical evaluation of 70 paraplegic patients. Orthopedics 20(5):411-418.
Speaker Presentations
Speaker PPTs Click Here




